
FHIRcast
Draft "Standard for Trial Use" (STU2) This is the draft of the 1.1 release of the FHIRcast specification. We are currently working towards a 1.1 release and would love your feedback and proposed changes. Look at our current issue list and get involved!
Overview
The FHIRcast specification describes the APIs used to synchronize disparate healthcare applications' user interfaces in real time, allowing them to show the same clinical content to a user (or group of users).
Once the subscribing app knows about the session, the app may subscribe to specific workflow-related events for the given session. The subscription is verified and the app is notified when those workflow-related events occur; for example, by the clinician opening a patient's chart. The subscribing app may initiate context changes by accessing APIs exposed by the Hub; for example, closing the patient's chart. The app deletes its subscription to no longer receive notifications. The notification message describing the workflow event is a simple json wrapper around one or more FHIR resources.
FHIRcast recommends the HL7 SMART on FHIR launch protocol for both session discovery and API authentication. FHIRcast enables a subscriber to receive notifications either through a webhook or over a websocket connection, and is modeled on the W3C WebSub RFC, such as its use of GET vs POST interactions and a Hub for managing subscriptions. The below flow diagram illustrates the series of interactions.
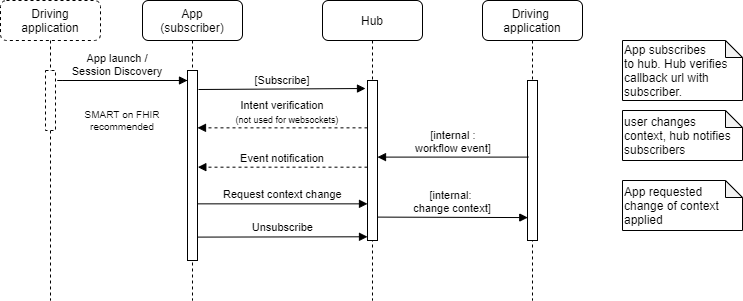
All data exchanged through the HTTP APIs SHALL be sent and received as JSON structures, and SHALL be transmitted over channels secured using the Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) over Transport Layer Security (TLS), also known as HTTPS and defined in RFC2818.
Session Discovery
A session is an abstract concept representing a shared workspace, such as user's login session over multiple applications or a shared view of one application distributed to multiple users. FHIRcast requires a session to have a unique, unguessable and opaque identifier. This identifier is exchanged as the value of the hub.topic parameter. Before establishing a subscription, an app must not only know the hub.topic, but also the the hub.url which contains the base url of the Hub.
Systems SHOULD use SMART on FHIR to authorize, authenticate and exchange initial shared context. If using SMART, following a SMART on FHIR EHR launch or SMART on FHIR standalone launch, the app SHALL request and, if authorized, SHALL be granted one or more fhircast OAuth 2.0 scopes. Accompanying this scope grant, the authorization server SHALL supply the hub.url and hub.topic SMART launch parameters alongside the access token and other parameters appropriate to establish initial shared context. Per SMART, when scopes of openid and fhirUser are granted, the authorization server additionally sends the current user's identity in an id_token.
Although FHIRcast works best with the SMART on FHIR launch and authorization process, implementation-specific launch, authentication, and authorization protocols may be possible. If not using SMART on FHIR, the mechanism enabling the app to discover the hub.url and hub.topic is not defined in FHIRcast. See other launch scenarios for guidance.
FHIRcast Authorization & SMART scopes
FHIRcast defines OAuth 2.0 access scopes that correspond directly to FHIRcast events. Our scopes associate read or write permissions to an event. Apps that need to receive workflow related events should ask for read scopes. Apps that request context changes should ask for write scopes. Hubs may decide what specific interactions and operations will be enabled by these scopes.
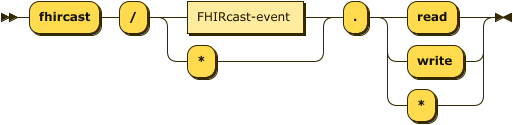
Expressed in EBNF notation, FHIRcast's scope syntax is:
scope ::= ( 'fhircast' ) '/' ( FHIRcast-event ) '.' ( 'read' | 'write' | '*' )
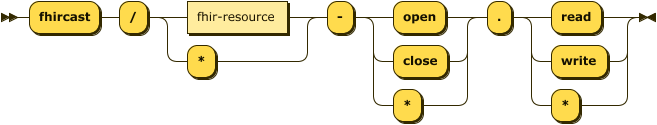
The FHIRcast event name is also a computable syntax, the complete syntax for FHIRcast scopes is:
scope ::= 'fhircast' '/' fhir-resource '-' ( 'open' | 'close' | '*' ) '.' ( 'read' | 'write' | '*' )
SMART Launch Example
Note that the SMART launch parameters include the Hub's base url and the session identifier in the hub.url and hub.topic fields.
{
"access_token": "i8hweunweunweofiwweoijewiwe",
"token_type": "bearer",
"patient": "123",
"expires_in": 3600,
"encounter": "456",
"imagingstudy": "789",
"hub.url" : "https://hub.example.com",
"hub.topic": "fdb2f928-5546-4f52-87a0-0648e9ded065",
}
Subscribing and Unsubscribing
Subscribing consists of two exchanges:
- Subscriber requests a subscription at the
hub.urlurl. - For
hub.channel.type=webhook, Hub confirms the subscription was actually requested by the subscriber by contacting thehub.callbackurl. - For
hub.channel.type=websocket, Hub returns a wss url and subscriber establishes websocket connection.
Unsubscribing works in the same way, except with a single parameter changed to indicate the desire to unsubscribe.
Subscription Request
To create a subscription, the subscribing app SHALL perform an HTTP POST (RFC7231) to the Hub's base url (as specified in hub.url) with the parameters in the table below.
This request SHALL have a Content-Type header of application/x-www-form-urlencoded and SHALL use the following parameters in its body, formatted accordingly:
| Field | Optionality | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
hub.channel.type |
Required | string | The subscriber SHALL specify a channel type of websocket or webhook. Subscription requests without this field SHOULD be rejected by the Hub. |
hub.mode |
Required | string | The literal string "subscribe" or "unsubscribe", depending on the goal of the request. |
hub.topic |
Required | string | The identifier of the user's session that the subscriber wishes to subscribe to or unsubscribe from. MAY be a guid. |
hub.events |
Required | string | Comma-separated list of event types from the Event Catalog for which the Subscriber wants notifications. |
hub.lease_seconds |
Optional | number | Number of seconds for which the subscriber would like to have the subscription active, given as a positive decimal integer. Hubs MAY choose to respect this value or not, depending on their own policies, and MAY set a default value if the subscriber omits the parameter. If using OAuth 2.0, the Hub SHALL limit the subscription lease seconds to be less than or equal to the access token's expiration. |
hub.callback |
Conditional | string | Required when hub.channel.type=webhook. SHALL not be present when hub.channel.type=websocket. The Subscriber's callback URL where notifications should be delivered. The callback URL SHOULD be an unguessable URL that is unique per subscription. |
hub.secret |
Conditional | string | Required when hub.channel.type=webhook. SHALL not be present when hub.channel.type=websocket. A subscriber-provided cryptographically random unique secret string that SHALL be used to compute an HMAC digest delivered in each notification. This parameter SHALL be less than 200 bytes in length. |
hub.channel.endpoint |
Conditional | string | Required when hub.channel.type=websocket for re-subscribes and unsubscribes. SHALL not be present when hub.channel.type=webhook. The wss url identifying an existing websocket subscription. |
If OAuth 2.0 authentication is used, this POST request SHALL contain the Bearer access token in the HTTP Authorization header.
Hubs SHALL allow subscribers to re-request subscriptions that are already activated. Each subsequent and verified request to a Hub to subscribe or unsubscribe SHALL override the previous subscription state for a specific hub.topic, hub.callback / hub.channel.endpoint url, and hub.events combination. For example, a subscriber MAY modify its subscription by subscribing to or unsubscribing from additional events by sending subscription requests for additional events with the same topic and callback/endpoint url.
The webhook callback URL MAY contain arbitrary query string parameters (e.g., ?foo=bar&red=fish). Hubs SHALL preserve the query string during subscription verification by appending new, Hub-defined, parameters to the end of the list using the & (ampersand) character to join. When sending the event notifications, the Hub SHALL make a POST request to the callback URL including any query string parameters in the URL portion of the request, not as POST body parameters.
The client that creates the subscription may not be the same system as the server hosting the callback url or connecting to the wss url. (For example, some type of federated authorization model could possibly exist between these two systems.) However, in FHIRcast, the Hub assumes that the same authorization and access rights apply to both the subscribing client and the system receiving notifications.
Subscription Response
If the Hub URL supports FHIRcast and is able to handle the subscription or unsubscription request, the Hub SHALL respond to a subscription request with an HTTP 202 "Accepted" response to indicate that the request was received and will now be verified by the Hub. If using websockets and supported by the Hub, the Content-Location HTTP header of the response SHALL contain a wss url. If webhooks, the Hub SHOULD perform the verification of intent as soon as possible. The websocket wss url SHALL be cryptographically random, unique and unguessable.
If a Hub finds any errors in the subscription request, an appropriate HTTP error response code (4xx or 5xx) SHALL be returned. In the event of an error, the Hub SHOULD return a description of the error in the response body as plain text, used to assist the client developer in understanding the error. This is not meant to be shown to the end user. Hubs MAY decide to reject some subscription requests based on their own policies.
webhook Subscription Request Example
In this example, the app asks to be notified of the patient-open and patient-close events.
POST https://hub.example.com
Host: hub.example.com
Authorization: Bearer i8hweunweunweofiwweoijewiwe
Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded
hub.channel.type=webhook&hub.callback=https%3A%2F%2Fapp.example.com%2Fsession%2Fcallback%2Fv7tfwuk17a&hub.mode=subscribe&hub.topic=fdb2f928-5546-4f52-87a0-0648e9ded065&hub.secret=shhh-this-is-a-secret&hub.events=patient-open,patient-close
webhook Subscription Response Example
HTTP/1.1 202 Accepted
websocket Initial Subscription Request Example
In this example, the app creates an initial subscription and asks to be notified of the patient-open and patient-close events.
POST https://hub.example.com
Host: hub.example.com
Authorization: Bearer i8hweunweunweofiwweoijewiwe
Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded
hub.channel.type=websocket&hub.mode=subscribe&hub.topic=fdb2f928-5546-4f52-87a0-0648e9ded065&hub.events=patient-open,patient-close
websocket Subscription Response Example
HTTP/1.1 202 Accepted
Content-Location: wss://hub.example.com/ee30d3b9-1558-464f-a299-cbad6f8135de
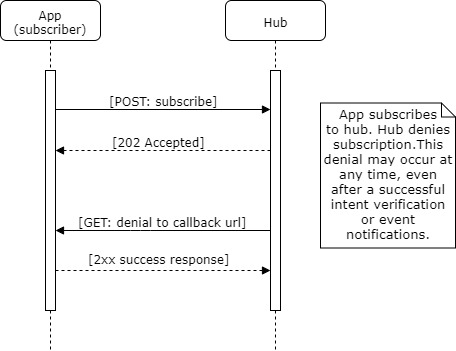
Subscription Denial
If (and when) the subscription is denied, the Hub SHALL inform the subscriber. This can occur when the subscription is requested for a variety of reasons, or it can occur after the subscription had already been accepted because the Hub no longer supports that subscription (e.g. it has expired). The communication mechanism for a subscription denial varies per hub.channel.type, but the information communicated from the Hub to the subscriber does not.
| Field | Optionality | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
hub.mode |
Required | string | The literal string "denied". |
hub.topic |
Required | string | The topic given in the corresponding subscription request. MAY be a guid. |
hub.events |
Required | string | A comma-separated list of events from the Event Catalog corresponding to the events string given in the corresponding subscription request, which are being denied. |
hub.reason |
Optional | string | The Hub may include a reason. The subscription MAY be denied by the Hub at any point (even if it was previously accepted). The Subscriber SHOULD then consider that the subscription is not possible anymore. |
The below webhook flow diagram and websocket flow diagram and examples illustrate the subscription denial sequence and message details.
webhook Subscription Denial
To deny a subscription with hub.channel.type=webhook, the Hub sends an HTTP GET request to the subscriber's callback URL as given in the subscription request. This request appends the fields as query string arguments. The subscriber SHALL respond with an HTTP success (2xx) code.
webhook Subscription Denial Sequence
webhook Subscription Denial Example
GET https://app.example.com/session/callback/v7tfwuk17a?hub.mode=denied&hub.topic=fdb2f928-5546-4f52-87a0-0648e9ded065hub.events=patient-open,patient-close&hub.reason=session+unexpectedly+stopped HTTP 1.1
Host: subscriber
websocket Subscription Denial
To deny a subscription with hub.channel.type=websocket, the Hub sends a json object to the subscriber through the established websocket connection.
websocketSubscription Denial Sequence
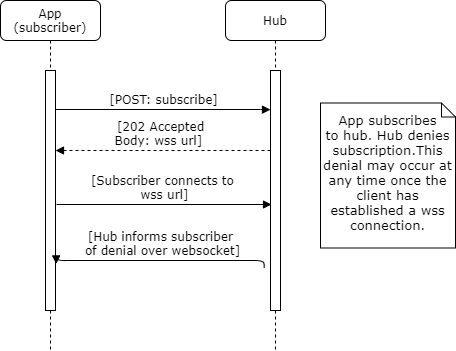
websocket Subscription Denial Example
{
"hub.mode": "denied",
"hub.topic":" "fba7b1e2-53e9-40aa-883a-2af57ab4e2c",
"hub.events": "patient-open,patient-close",
"hub.reason": "session unexpectedly stopped"
}
Subscription Confirmation
If a subscription or unsubscription is not denied, the Hub SHALL confirm the subscription. For hub.channel.type=webhook, the confirmation verifies the intent of the subscriber and ensures that the subscriber actually controls the callback url. For hub.channel.types of both webhook and websocket, this subscription confirmation step informs the subscriber of the details of Hub's recently created subscription.
webhook Intent Verification Request
In order to prevent an attacker from creating unwanted subscriptions on behalf of a subscriber (or unsubscribing desired ones), a Hub must ensure that a webhook subscriber did indeed send the subscription request. The Hub SHALL verify a subscription request by sending an HTTPS GET request to the subscriber's callback URL as given in the subscription request. This request SHALL have the following query string arguments appended
| Field | Optionality | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
hub.mode |
Required | string | The literal string "subscribe" or "unsubscribe", which matches the original request to the Hub from the subscriber. |
hub.topic |
Required | string | The session topic given in the corresponding subscription request. MAY be a guid. |
hub.events |
Required | string | A comma-separated list of events from the Event Catalog corresponding to the events string given in the corresponding subscription request. |
hub.challenge |
Required | string | A Hub-generated, random string that SHALL be echoed by the subscriber to verify the subscription. |
hub.lease_seconds |
Required | number | The Hub-determined number of seconds that the subscription will stay active before expiring, measured from the time the verification request was made from the Hub to the subscriber. If provided to the client, the Hub SHALL unsubscribe the client once lease_seconds has expired and MAY send a subscription denial. If the subscriber wishes to continue the subscription it MAY resubscribe. |
webhook Intent Verification Request Example
GET https://app.example.com/session/callback/v7tfwuk17a?hub.mode=subscribe&hub.topic=fdb2f928-5546-4f52-87a0-0648e9ded065&hub.events=patient-open,patient-close&hub.challenge=meu3we944ix80ox&hub.lease_seconds=7200 HTTP 1.1
Host: subscriber
webhook Intent Verification Response
If the hub.topic of the Intent Verification Request corresponds to a pending subscription or unsubscription that the subscriber wishes to carry out it SHALL respond with an HTTP success (2xx) code, a header of Content-Type: text/html, and a response body equal to the hub.challenge parameter. If the subscriber does not agree with the action, the subscriber SHALL respond with a 404 "Not Found" response.
The Hub SHALL consider other server response codes (3xx, 4xx, 5xx) to mean that the verification request has failed. If the subscriber returns an HTTP success (2xx) but the content body does not match the hub.challenge parameter, the Hub SHALL also consider verification to have failed.
The below flow diagram and example illustrate the successful subscription sequence and message details.
webhook Successful Subscription Sequence
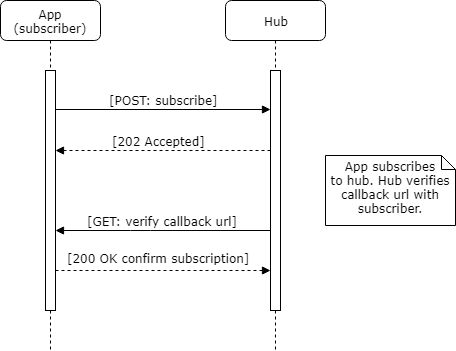
webhook Intent Verification Response Example
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
Content-Type: text/html
meu3we944ix80ox
NOTE The spec uses GET vs POST to differentiate between the confirmation/denial of the subscription request and delivering the content. While this is not considered "best practice" from a web architecture perspective, it does make implementation of the callback URL simpler. Since the POST body of the content distribution request may be any arbitrary content type and only includes the actual content of the document, using the GET vs POST distinction to switch between handling these two modes makes implementations simpler.
websocket Subscription Confirmation
To confirm a subscription request, upon the subscriber establishing a websocket connection to the hub.channel.endpoint wss url, the Hub SHALL send a confirmation. This confirmation includes the following elements:
| Field | Optionality | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
hub.mode |
Required | string | The literal string "subscribe". |
hub.topic |
Required | string | The session topic given in the corresponding subscription request. |
hub.events |
Required | string | A comma-separated list of events from the Event Catalog corresponding to the events string given in the corresponding subscription request. |
hub.lease_seconds |
Required | number | The Hub-determined number of seconds that the subscription will stay active before expiring, measured from the time the verification request was made from the Hub to the subscriber. If provided to the client, the Hub SHALL unsubscribe the client once lease_seconds has expired and MAY send a subscription denial. If the subscriber wishes to continue the subscription it MAY resubscribe. |
websocket Intent Verification Request Example
{
"hub.mode": "subscribe",
"hub.topic": "fdb2f928-5546-4f52-87a0-0648e9ded065",
"hub.events": "patient-open,patient-close",
"hub.lease-seconds": 7200
}
Unsubscribe
Once a subscribing app no longer wants to receive event notifications, it SHALL unsubscribe from the session. The unsubscribe request message mirrors the subscribe request message. To unsubscribe, the hub.mode SHALL be equal to the lowercase string unsubscribe. Only unsubscribes for hub.channel.type=webhook SHALL include the hub.callback, hub.secret, and hub.challenge. Only unsubscribes for hub.channel.type=websocket SHALL include the wss websocket url in hub.channel.endpoint. Note that the unsubscribe request is performed over HTTP, even for subscriptions using websockets.
| Field | Optionality | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
hub.channel.type |
Required | string | The subscriber SHALL specify a channel type of websocket or webhook. Subscription requests without this field SHOULD be rejected by the Hub. |
hub.mode |
Required | string | The literal string "unsubscribe". |
hub.topic |
Required | string | The identifier of the user's session that the subscriber wishes to subscribe to or unsubscribe from. MAY be a guid. |
hub.events |
Required | string | Comma-separated list of event types from the Event Catalog for which the Subscriber no longer wants notifications. |
hub.callback |
Conditional | string | Required when hub.channel.type=webhook. SHALL not be present when hub.channel.type=websocket. |
hub.secret |
Conditional | string | Required when hub.channel.type=webhook. SHALL not be present when hub.channel.type=websocket. A subscriber-provided cryptographically random unique secret string that SHALL be used to compute an HMAC digest delivered in each notification. This parameter SHALL be less than 200 bytes in length. |
hub.challenge |
Conditional | string | Required when hub.channel.type=webhook. SHALL not be present when hub.channel.type=websocket. A Hub-generated, random string communicated during Intent Verification. |
hub.channel.endpoint |
Conditional | string | Required when hub.channel.type=websocket for re-subscribes and unsubscribes. SHALL not be present when hub.channel.type=webhook. The wss url identifying an existing websocket subscription. |
webhook Unsubscribe Request Example
POST https://hub.example.com
Host: hub
Authorization: Bearer i8hweunweunweofiwweoijewiwe
Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded
hub.channel.type=webhook&hub.callback=https%3A%2F%2Fapp.example.com%2Fsession%2Fcallback%2Fv7tfwuk17a&hub.mode=unsubscribe&hub.topic=fdb2f928-5546-4f52-87a0-0648e9ded065&hub.secret=shhh-this-is-a-secret&hub.events=patient-open,patient-close&hub.challenge=meu3we944ix80ox
websocket Unsubscribe Request Example
POST https://hub.example.com
Host: hub
Authorization: Bearer i8hweunweunweofiwweoijewiwe
Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded
hub.channel.type=websocket&hub.channel.endpoint=wss%3A%2F%2Fhub.example.com%2Fee30d3b9-1558-464f-a299-cbad6f8135de%0A&hub.mode=unsubscribe&hub.topic=fdb2f928-5546-4f52-87a0-0648e9ded065&hub.events=patient-open,patient-close
Event Notification
The Hub SHALL notify subscribed apps of workflow-related events to which the app is subscribed. The notification is a JSON object communicated over the a webhook or websocket channel.
webhook vs websocket
A subsciber specifies the preferred hub.channel.type of either webhook or websocket during creation of its subscription. Only the event notification and subscription denied exchanges are affected by the channel type. Subscribers SHOULD use websockets when they are unable to host an accessible callback url.
Implementer feedback is solicited around the preference and desired optionality of webhooks and websockets.
Event Notification Request
The notification to the subscriber SHALL include a description of the subscribed event that just occurred, an ISO 8601-2 formatted timestamp in UTC and an event identifier that is universally unique for the Hub. The timestamp MAY be used by subscribers to establish message affinity (message ordering) through the use of a message queue. The event identifier MAY be used to differentiate retried messages from user actions.
Event Notification Request Details
The notification's hub.event and context fields inform the subscriber of the current state of the user's session. The hub.event is a user workflow event, from the Event Catalog (or an organization-specific event in reverse-domain name notation). The context is an array of named FHIR resources (similar to CDS Hooks's context field) that describe the current content of the user's session. Each event in the Event Catalog defines what context is expected in the notification. Hubs MAY use the FHIR _elements parameter to limit the size of the data being passed while also including additional, local identifiers that are likely already in use in production implementations. Subscribers SHALL accept a full FHIR resource or the _elements-limited resource as defined in the Event Catalog.
| Field | Optionality | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
timestamp |
Required | string | ISO 8601-2 timestamp in UTC describing the time at which the event occurred with subsecond accuracy. |
id |
Required | string | Event identifier used to recognize retried notifications. This id SHALL be unique for the Hub, for example a GUID. |
event |
Required | object | A json object describing the event. See below. |
| Field | Optionality | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
hub.topic |
Required | string | The session topic given in the subscription request. MAY be a guid. |
hub.event |
Required | string | The event that triggered this notification, taken from the list of events from the subscription request. |
context |
Required | array | An array of named FHIR objects corresponding to the user's context after the given event has occurred. Common FHIR resources are: Patient, Encounter, ImagingStudy and List. The Hub SHALL only return FHIR resources that are authorized to be accessed with the existing OAuth 2.0 access_token. |
webhook Event Notification Request Details
Only for subscriptions with hub.channel.type=webhook, using the hub.secret from the subscription request, the Hub SHALL generate an HMAC signature of the payload and include that signature in the request headers of the notification. The X-Hub-Signature header's value SHALL be in the form method=signature where method is one of the recognized algorithm names and signature is the hexadecimal representation of the signature. The signature SHALL be computed using the HMAC algorithm (RFC6151) with the request body as the data and the hub.secret as the key.
POST https://app.example.com/session/callback/v7tfwuk17a HTTP/1.1
Host: subscriber
X-Hub-Signature: sha256=dce85dc8dfde2426079063ad413268ac72dcf845f9f923193285e693be6ff3ae
<json object>
Event Notification Request Example
For both webhook and websocket subscriptions, the event notification content is the same.
{
"timestamp": "2018-01-08T01:37:05.14",
"id": "q9v3jubddqt63n1",
"event": {
"hub.topic": "fdb2f928-5546-4f52-87a0-0648e9ded065",
"hub.event": "patient-open",
"context": [
{
"key": "patient",
"resource": {
"resourceType": "Patient",
"id": "ewUbXT9RWEbSj5wPEdgRaBw3",
"identifier": [
{
"type": {
"coding": [
{
"system": "http://terminology.hl7.org/CodeSystem/v2-0203",
"value": "MR",
"display": "Medication Record Number"
}
"text": "MRN"
]
}
}
]
}
}
]
}
}
Event Notification Response
The subscriber SHALL respond to the notification with an appropriate HTTP status code. In the case of a successful notification, the subscriber SHALL respond with an HTTP [RFC7231] 2xx response code to indicate a success; otherwise, the subscriber SHALL respond with an HTTP error status code. The Hub MAY use these statuses to track synchronization state.
webhook Event Notification Response Example
For webhook subscriptions, the HTTP status code is communicated in the HTTP response, as expected.
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
websocket Event Notification Response Example
For websocket subscriptions, the id of the event notification and the HTTP status code is communicated from the client to Hub through the existing websocket channel, wrapped in a json object. Since the websocket channel does not have a synchronous request/response, this id is necessary for the Hub to correlate the response to the correct notification.
Feedback from implementers is requested here. This is the only proposed communication from the subscriber to the Hub over websockets and the use of an HTTP status within a websocket connection, wrapped in json is weird. However, it seems important to enable the Hub to optionally track and/or broadcast synchronization state.
| Field | Optionality | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
id |
Required | string | Event identifier from the event notification to which this response corresponds. |
status |
Required | numeric HTTP status code | Numeric HTTP [RFC7231] response code to indicate success or failure of the event notification within the subscribing app. Any 2xx code indicates success, any other code indicates failure. |
{
"id": "q9v3jubddqt63n1",
"status": "200"
}
Event Notification Errors
All standard events are defined outside of the base FHIRcast specification in the Event Catalog with the single exception of the infrastructural syncerror event.
If the subscriber cannot follow the context of the event, for instance due to an error or a deliberate choice to not follow a context, the subscriber SHALL respond with an HTTP error status code as described in Event Notification Response. If the Hub does not receive a successful HTTP status from a event notification, it SHOULD generate a syncerror event to the other subscribers of that topic. A syncerror notification has the same structure as the other event notification with a single FHIR OperationOutcome as the event's context.
Event Notification Error Request
Request Context Change Parameters
| Field | Optionality | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
timestamp |
Required | string | ISO 8601-2 timestamp in UTC describing the time at which the event occurred with subsecond accuracy. |
id |
Required | string | Event identifier, which MAY be used to recognize retried notifications. This id SHALL be unique and could be a GUID. This id SHOULD be re-used from the previous event communicated to subscribers related to the synchronization failure. |
event |
Required | object | A json object describing the event. See below. |
Event Notification Error Event Object Parameters
| Field | Optionality | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
hub.topic |
Required | string | The session topic given in the subscription request. |
hub.event |
Required | string | Shall be the string syncerror. |
context |
Required | array | An array containing a single FHIR OperationOutcome. The OperationOutcome SHALL use a code of processing. |
Event Notification Error Example
POST https://hub.example.com/7jaa86kgdudewiaq0wtu HTTP/1.1
Host: hub
Authorization: Bearer i8hweunweunweofiwweoijewiwe
Content-Type: application/json
{
"timestamp": "2018-01-08T01:37:05.14",
"id": "q9v3jubddqt63n1",
"event": {
"hub.topic": "fdb2f928-5546-4f52-87a0-0648e9ded065",
"hub.event": "syncerror",
"context": [
{
"key": "operationoutcome",
"resource": {
"resourceType": "OperationOutcome",
"issue": [
{
"severity": "warning",
"code": "processing",
"diagnostics": "AppId3456 failed to follow context"
}
]
}
}
]
}
}
Request Context Change
Similar to the Hub's notifications to the subscriber, the subscriber MAY request context changes with an HTTP POST to the hub.url. The Hub SHALL either accept this context change by responding with any successful HTTP status or reject it by responding with any 4xx or 5xx HTTP status. The subscriber SHALL be capable of gracefully handling a rejected context request.
Once a requested context change is accepted, the Hub SHALL broadcast the context notification to all subscribers, including the original requestor.
Request Context Change Request
Request Context Change Parameters
| Field | Optionality | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
timestamp |
Required | string | ISO 8601-2 timestamp in UTC describing the time at which the event occurred with subsecond accuracy. |
id |
Required | string | Event identifier, which MAY be used to recognize retried notifications. This id SHALL be uniquely generated by the subscriber and could be a GUID. Following an accepted context change request, the Hub MAY re-use this value in the broadcasted event notifications. |
event |
Required | object | A json object describing the event. See below. |
Request Context Change Event Object Parameters
| Field | Optionality | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
hub.topic |
Required | string | The session topic given in the subscription request. |
hub.event |
Required | string | The event that triggered this request for the subscriber, taken from the list of events from the subscription request. |
context |
Required | array | An array of named FHIR objects corresponding to the user's context after the given event has occurred. Common FHIR resources are: Patient, Encounter, ImagingStudy and List. |
POST https://hub.example.com/7jaa86kgdudewiaq0wtu HTTP/1.1
Host: hub
Authorization: Bearer i8hweunweunweofiwweoijewiwe
Content-Type: application/json
{
"timestamp": "2018-01-08T01:40:05.14",
"id": "wYXStHqxFQyHFELh",
"event": {
"hub.topic": "fdb2f928-5546-4f52-87a0-0648e9ded065",
"hub.event": "close-patient-chart",
"context": [
{
"key": "patient",
"resource": {
"resourceType": "Patient",
"id": "798E4MyMcpCWHab9",
"identifier": [
{
"type": {
"coding": [
{
"system": "http://terminology.hl7.org/CodeSystem/v2-0203",
"value": "MR",
"display": "Medication Record Number"
}
"text": "MRN"
]
}
}
]
}
}
]
}
}
Events
FHIRcast describes an workflow event subscription and notification scheme towards the goal of improving a clinician's workflow across multiple disparate applications. The set of events defined here are not a closed set; anyone is able to define new events to fit their use cases and propose those events to the community.
New events are proposed in a prescribed format using the documentation template by submitting a pull request. FHIRcast events are versioned, and mature according to the Event Maturity Model.
FHIRcast events are stateless. Context changes are a complete replacement of any previously communicated context, not "deltas". Understanding an event SHALL not require receiving a previous or future event.
Event Definition Format
Each event definition, specifies a single event name, a description of the workflow in which the event occurs, and contextual information associated with the event. FHIR is the interoperable data model used by FHIRcast. The context information associated with an event is communicated as subsets of FHIR resources. Event notifications SHALL include the elements of the FHIR resources defined in the context from the event definition. Event notification MAY include other elements of these resources. The source of these resources is the application's context or the FHIR server. The Hub SHALL return FHIR resources from the application's context. If the resource is not part of the application's context, it SHALL read them from the FHIR server.
For example, when the ImagingStudy-open event occurs, the notification sent to a subscriber SHALL include the ImagingStudy FHIR resource. Hubs should send the results of an ImagingStudy FHIR read using the _elements query parameter, like so: ImagingStudy/{id}?_elements=identifier,accession and in accordance with the FHIR specification.
A Hub may not support the _elements query parameter; a subscriber SHALL gracefully handle receiving a full FHIR resource in the context of a notification.
Each defined event in the standard event catalog SHALL be defined in the following format.
Event Definition Format: hook-name
Most FHIRcast events conform to an extensible syntax based upon FHIR resources. In the rare case where the FHIR data model doesn't describe content in the session, FHIRcast events MAY be statically named. For example, FHIR doesn't cleanly contain the concept of a user or user's session.
FHIRcast events SHOULD conform to this extensible syntax, patterned after the SMART on FHIR scope syntax. Expressed in EBNF notation, the FHIRcast syntax for workflow related events is:
hub.events ::= ( fhir-resource ) '-' ( 'open' | 'close' | '*' )
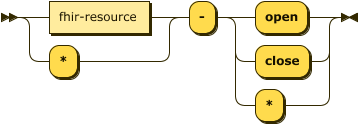
Event names are unique and case-insensitive. Statically named events, specific to an organization, SHALL be named with reverse domain notation (e.g. org.example.patient-transmogrify). Reverse domain notation SHALL not be used by a standard event catalog. Statically named events SHALL not contain a dash ("-").
Event Definition Format: Workflow
Describe the workflow in which the event occurs. Event creators SHOULD include as much detail and clarity as possible to minimize any ambiguity or confusion amongst implementors.
Event Definition Format: Context
Describe the set of contextual data associated with this event. Only data logically and necessarily associated with the purpose of this workflow related event should be represented in context. An event SHALL contain all required data fields, MAY contain optional data fields and SHALL not contain any additional fields.
All fields available within an event's context SHALL be defined in a table where each field is described by the following attributes:
- Key: The name of the field in the context JSON object. Event authors SHOULD name their context fields to be consistent with other existing events when referring to the same context field.
- Optionality: A string value of either
REQUIRED,OPTIONALorRequired, if exists - FHIR operation to generate context: A FHIR read or search string illustrating the intended content of the event.
- Description: A functional description of the context value. If this value can change according to the FHIR version in use, the description SHOULD describe the value for each supported FHIR version.
Event Maturity Model
The intent of the FHIRcast Event Maturity Model is to attain broad community engagement and consensus, before an event is labeled as mature, and to ensure that the event is necessary, implementable, and worthwhile to the systems that would reasonably be expected to use it. Implementer feedback should drive the maturity of new events. Diverse participation in open developer forums and events, such as HL7 FHIR Connectathons, is necessary to achieve significant implementer feedback. The below criteria will be evaluated with these goals in mind.
| Maturity Level | Maturity title | Requirements |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | Draft | Event is correctly named and defined per the FHIRcast event template. |
| 1 | Submitted | The above, and … Event definition is written up as a pull request using the Event template and community feedback is solicited from the community (e.g. the zulip FHIRcast stream](https://chat.fhir.org/#narrow/stream/179271-FHIRcast)). |
| 2 | Tested | The above, and … The event has been tested and successfully supports interoperability among at least one Hub and two independent subscribing apps using semi-realistic data and scenarios (e.g. at a FHIR Connectathon). The github pull request defining the event is approved and published. |
| 3 | Considered | The above, and … At least 3 distinct organizations recorded ten distinct implementer comments (including a github issue, tracker item, or comment on the event definition page), including at least two Hubs and three subscribing apps. The event has been tested at two connectathons. |
| 4 | Documented | The above, and … The author agrees that the artifact is sufficiently stable to require implementer consultation for subsequent non-backward compatible changes. The event is implemented in the standard FHIRcast reference implementation and multiple prototype projects. The Event specification SHALL:
|
| 5 | Mature | The above, and ... The event has been implemented in production in at least two Hubs and three independent subscribing apps. An HL7 working group ballots the event and the event has passed HL7 STU ballot. |
| 6 | Normative | The above, and ... the responsible HL7 working group and the sponsoring working group agree the material is ready to lock down and the event has passed HL7 normative ballot |
Event Maturity
As each event progresses through a process of being defined, tested, implemented, used in production environments, and balloted, the event's formal maturity level increases. Each event has its own maturity level, which SHALL be defined in the event's definition and correspond to the Event Maturity Model.
Change Log
Changes made to an event's definition SHALL be documented in a change log to ensure event consumers can track what has been changed over the life of an event. The change log SHALL contain the following elements:
- Version: The version of the change
- Description: A description of the change and its impact
For example:
| Version | Description |
|---|---|
| 1.1 | Added new context FHIR object |
| 1.0.1 | Clarified workflow description |
| 1.0 | Initial Release |
| --- |